Network Diagnostic tool
#Ping uses timed IP/ICMP
ECHO_REQUEST and ECHO_REPLY packets to probe the "distance" to the
target machine and since it's inception it's been part of Berkeley UNIX, many OS like Microsoft, Mac OS
Ping [Packet InterNet Grouper] can
be very useful Internet network diagnostic tests.
Steps to be followed while troubleshooting Network Issue's
Ping the localhost: Ping to 127.0.0.1 address will always ping
yourself,
1) You can check Ethernet adapter is Fine or Malfunctioning.
2) Also check TCP/IP Stack is installed on local PC
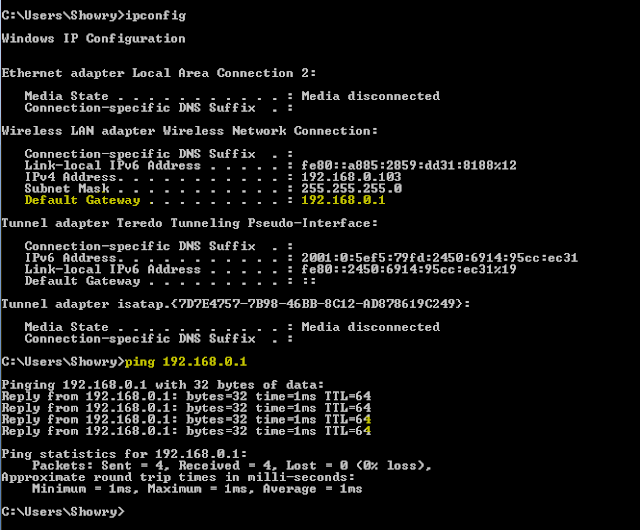
Ping the Default Gateway: Ping to default
gateway address will always network interface is up and has default route ( you can get Default gateway in ifconfig
or ipconfig command )
1) Incase ICMP is blocked using firewall you cannot get response back.
Ping to Check Internet / Intranet servers: Ping to see if you can reach another computer internet / intranet (8.8.8.8 google DNS server).
1) You test whether host is alive and current time taken to respond back to ping.
Ping to check domain is UP & Get Domain IP address : Ping can be used to probe domain is UP and
get domain IP address.
1) Check whether domain is up.
2) You can get the IP address of the domain.
Ping Life Cycle: You can use the Ping command to determine how long it takes to bounce a packet off of another site, which tells you its Internet distance in network terms
- Source sends an ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to the destination.
- Ping program initialize an SEQUENCE ID which increments with each ICMP
ECHO_REQUEST
- Ping initializes TTL (Time-to-live) period.
- Ping also inserts the sending time in the data section of the ECHO_REQUEST.
- Ping calculates ROUND_TRIPTIME, when host is responds with ICMP ECHO_REPLY back
to the source.
- Ping with new ICMP ECHO_REQUEST increments the sequence identifier till user
specified or default.
Ping statistics: Ping percentage of packet loss number of packets transmitted, number of
packets received, percentage of packet loss & round-trip time minimum,
average and maximum.